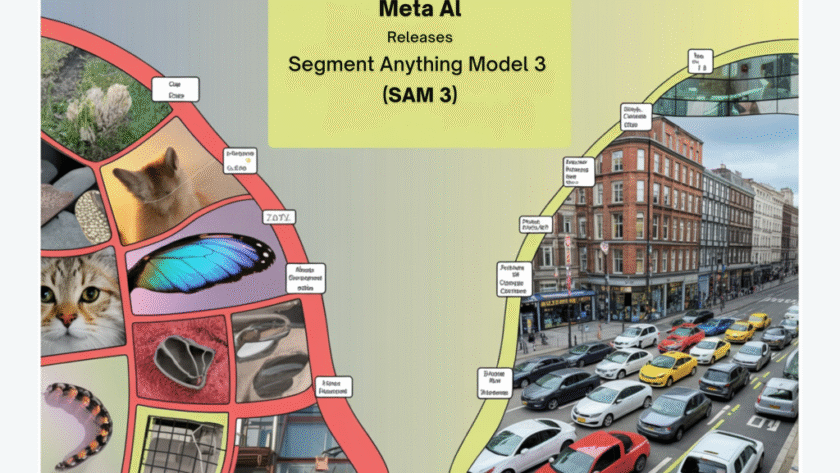
Salesforce AI research team present FOFPred, a language driven future optical flow prediction framework that connects large vision language models with diffusion transformers for dense motion forecasting in control and video generation settings. FOFPred takes one or more images and a natural language instruction such as ‘moving the bottle from right to left’ and predicts…