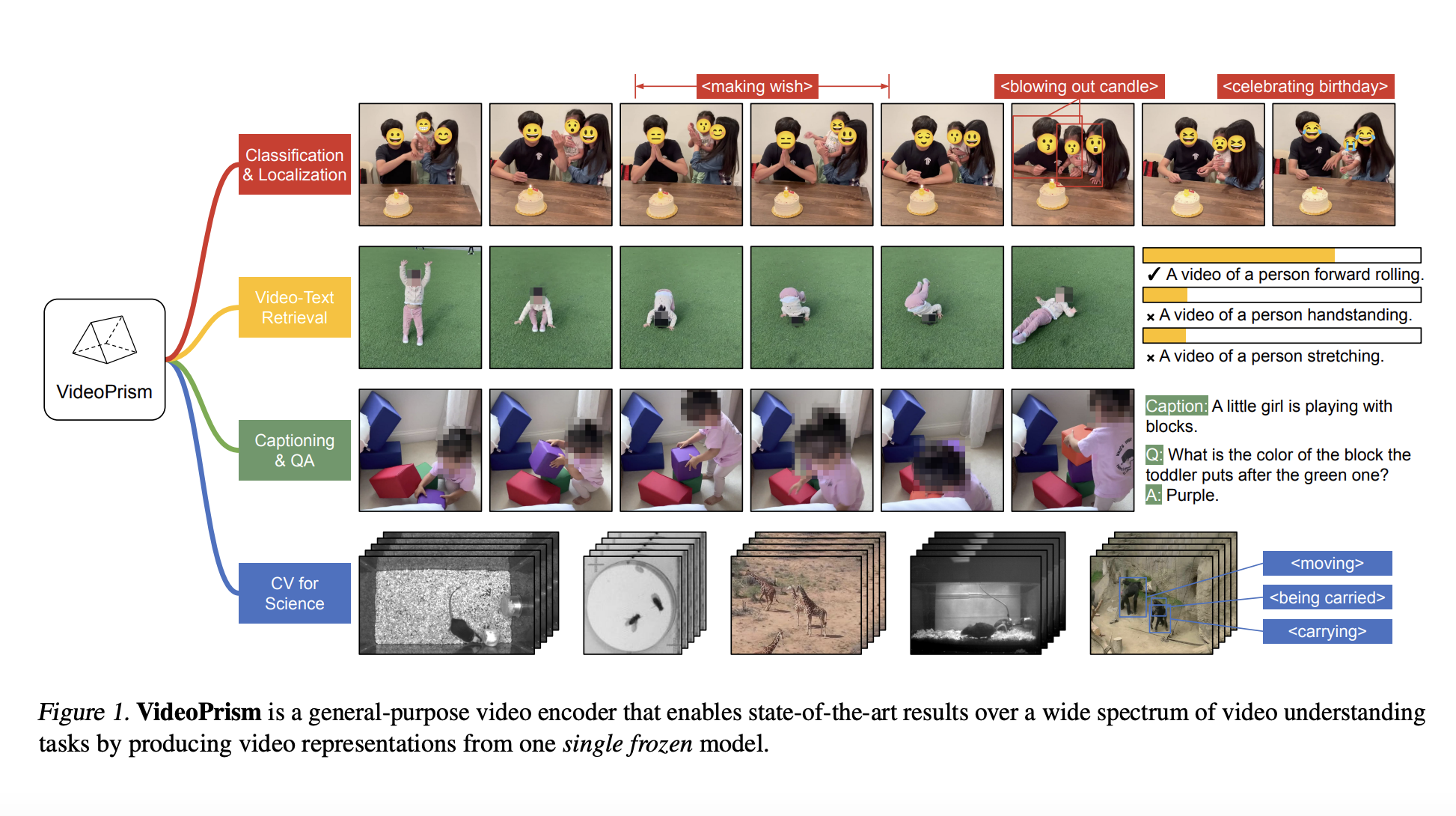
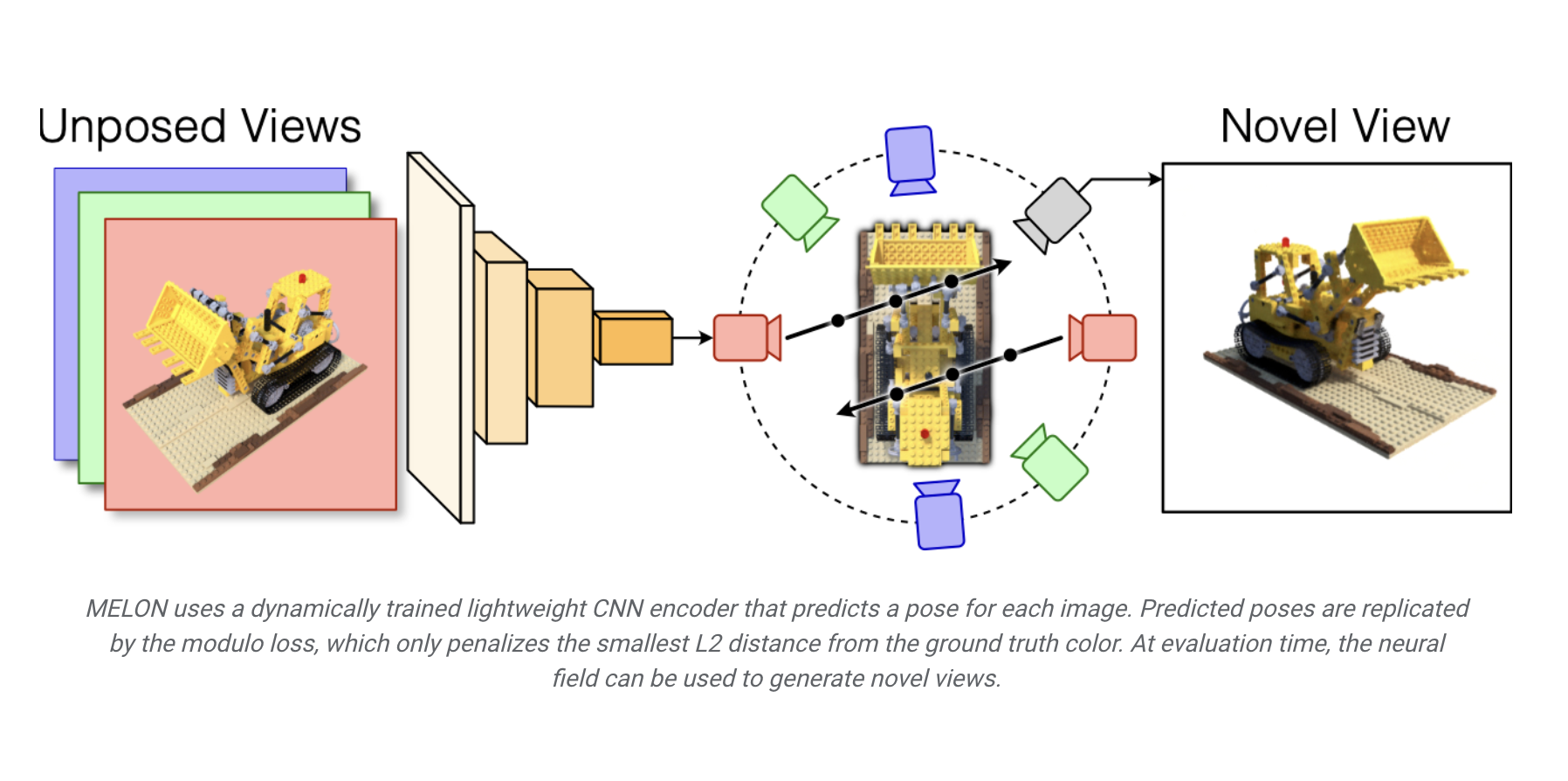
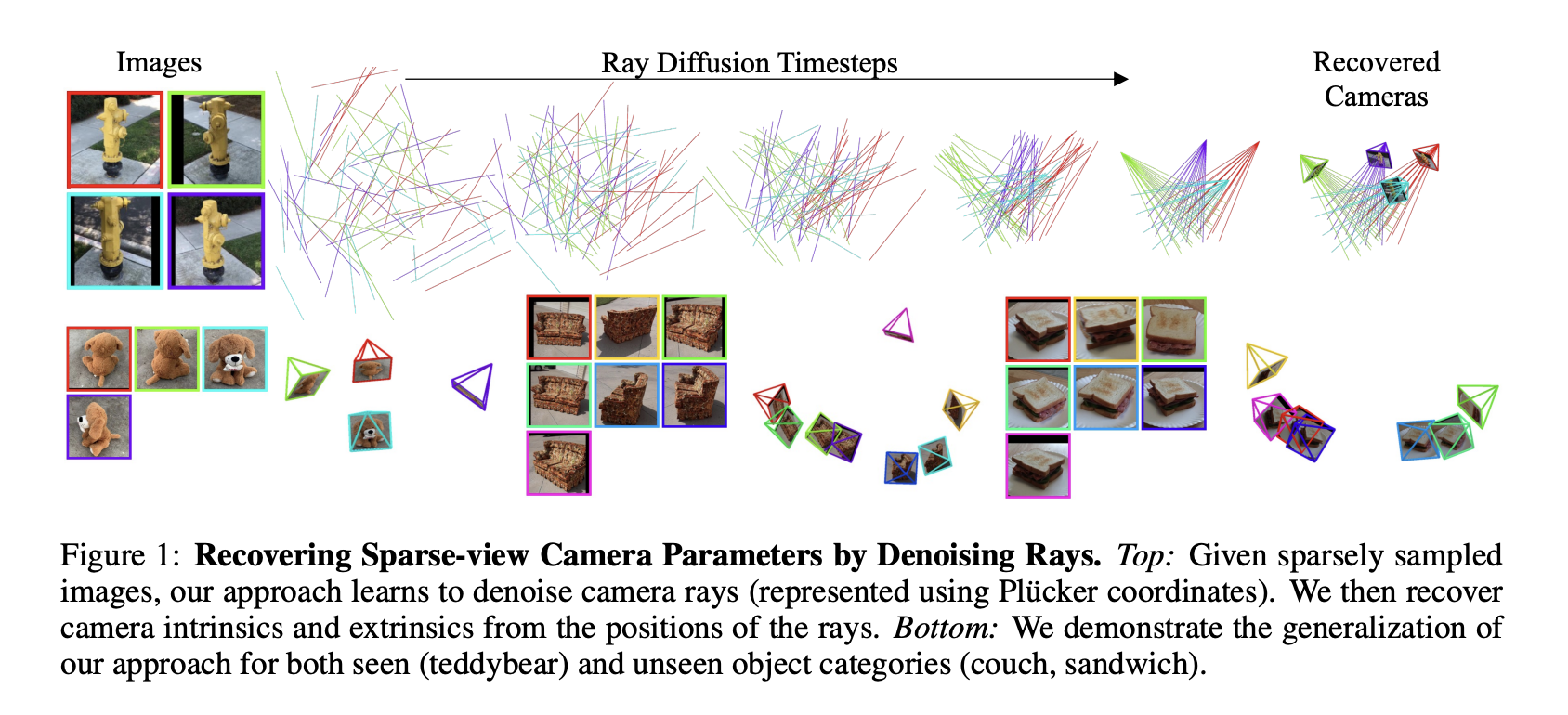
While humans can easily infer the shape of an object from 2D images, computers struggle to reconstruct accurate 3D models without knowledge of the camera poses. This problem, known as pose inference, is crucial for various applications, like creating 3D models for e-commerce and aiding autonomous vehicle navigation. Existing techniques relying on either gathering the…