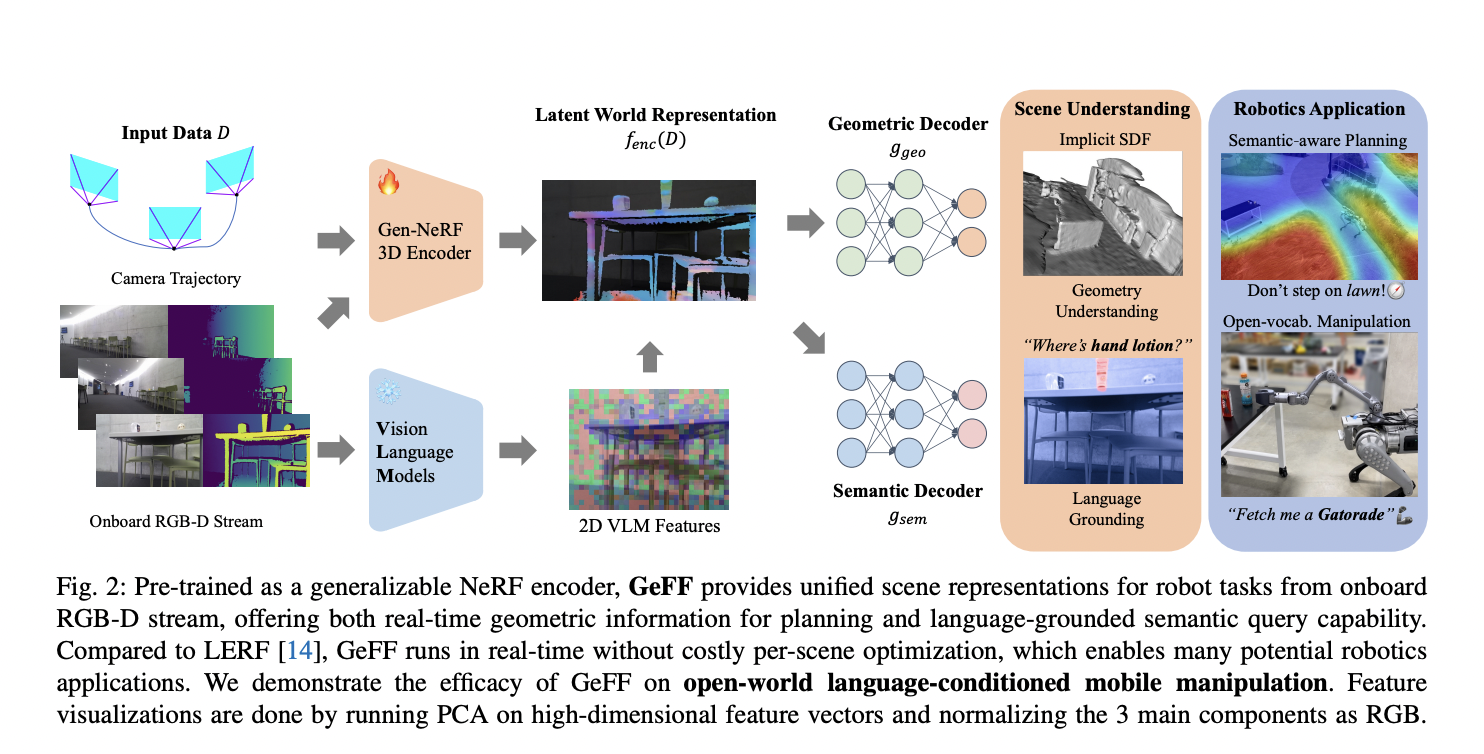
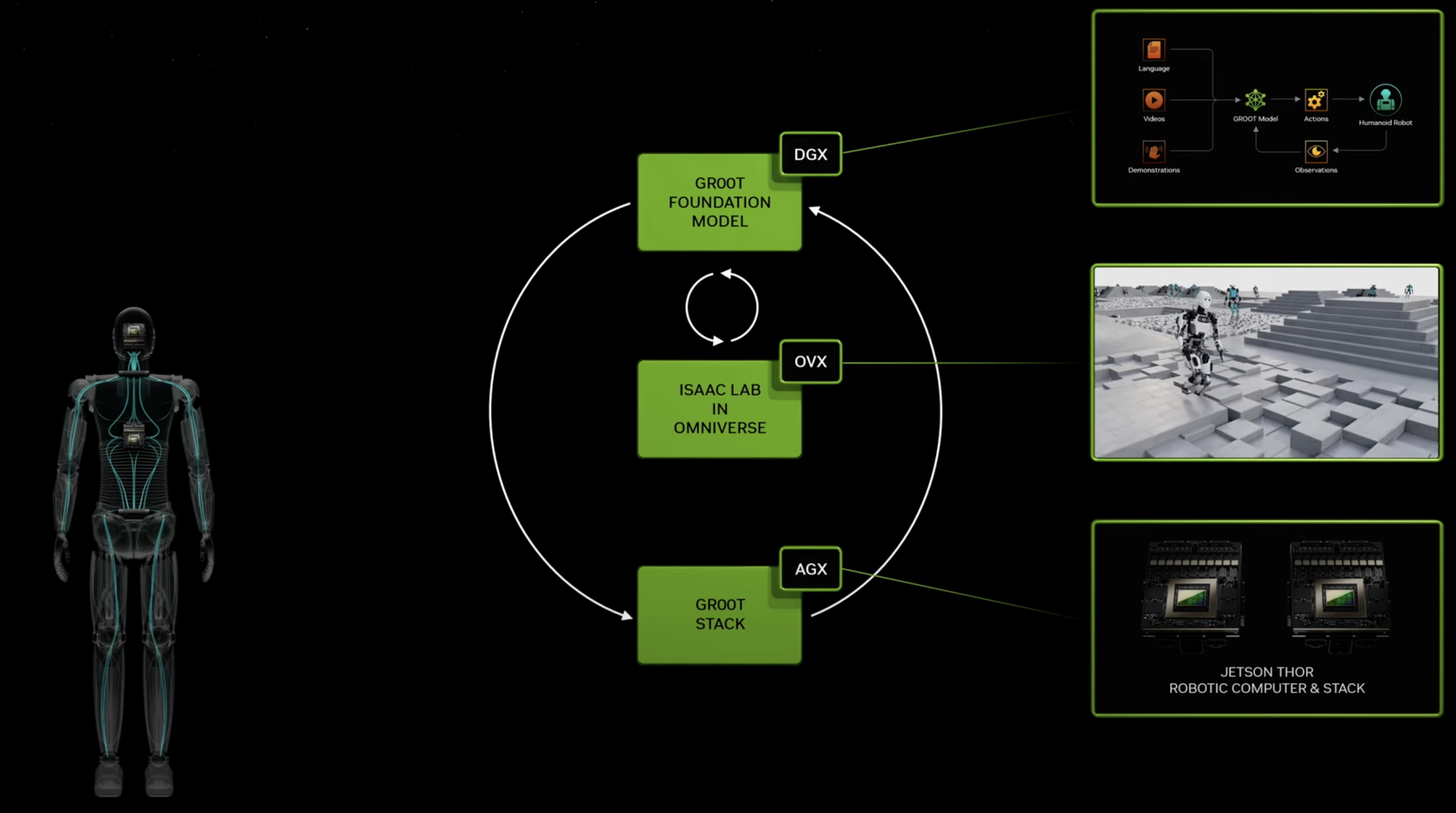
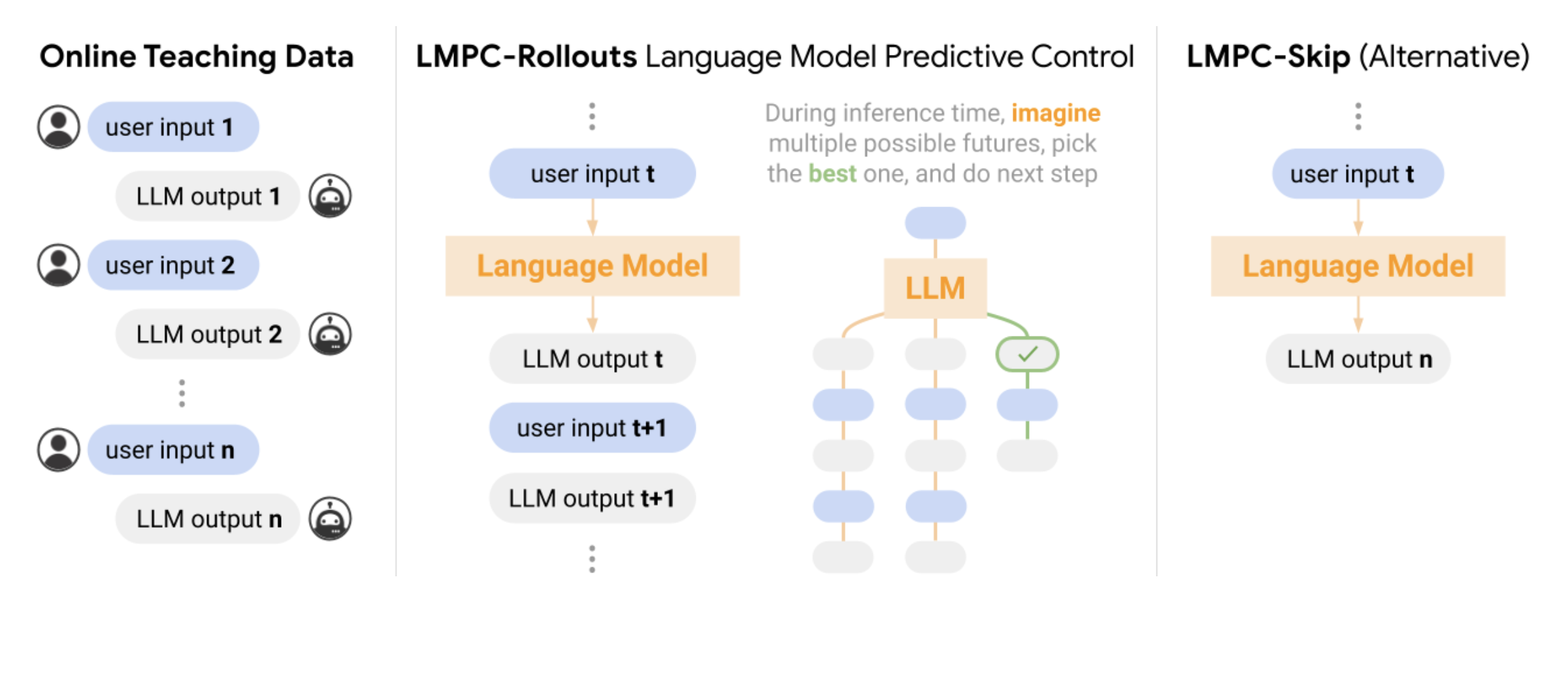
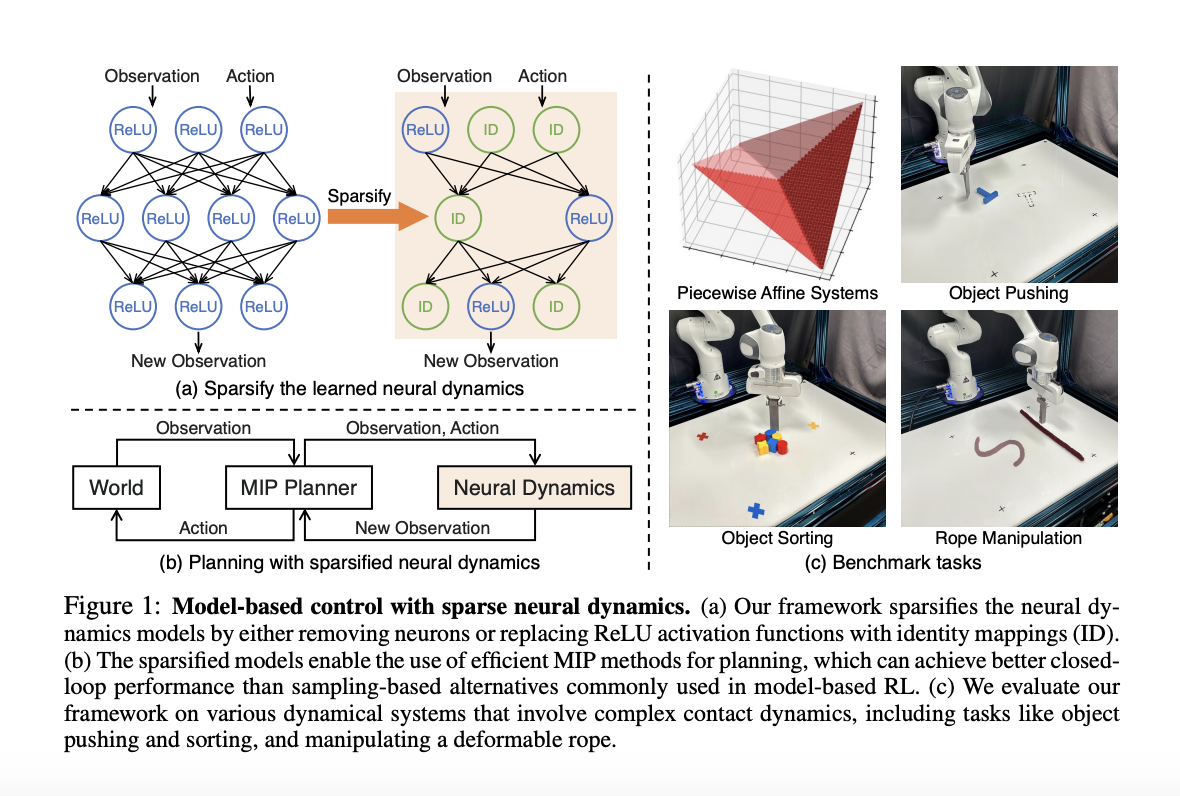
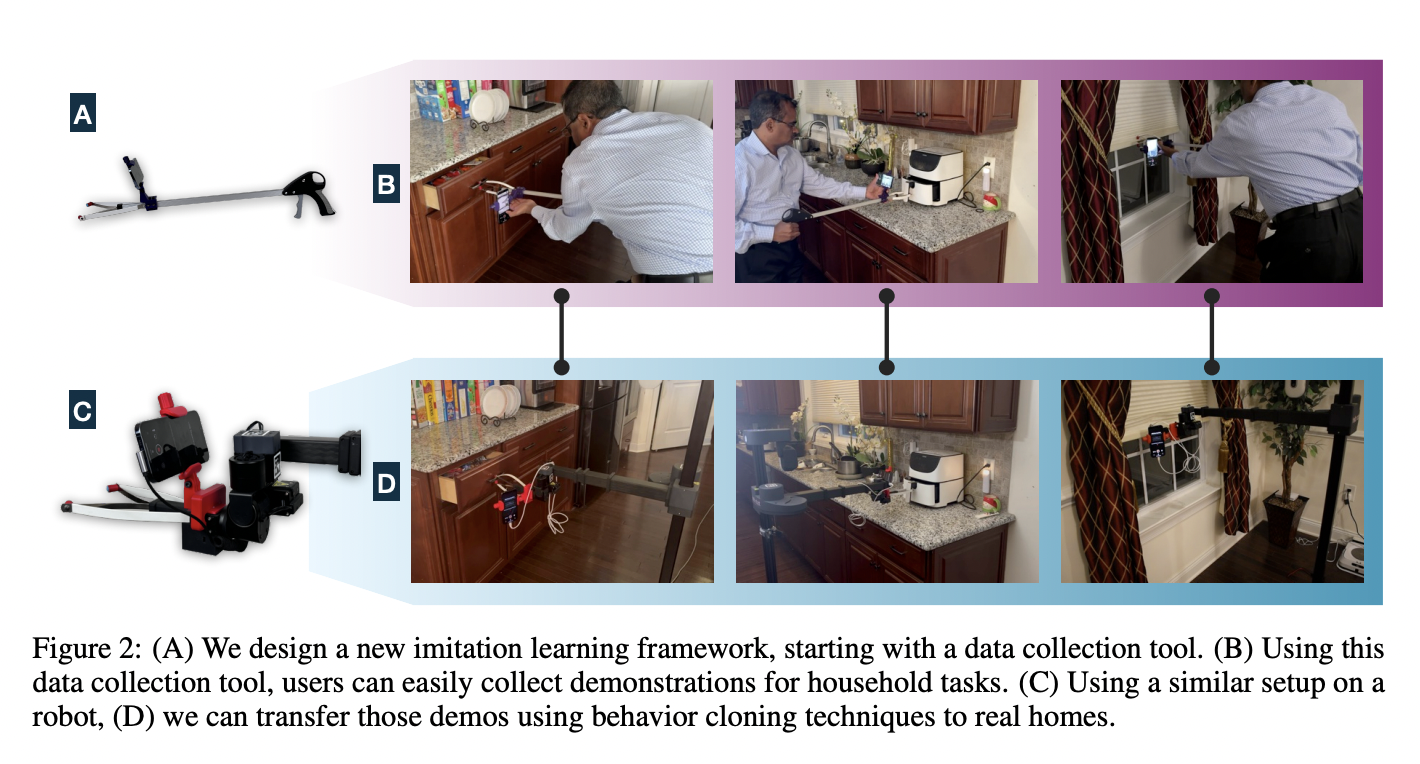
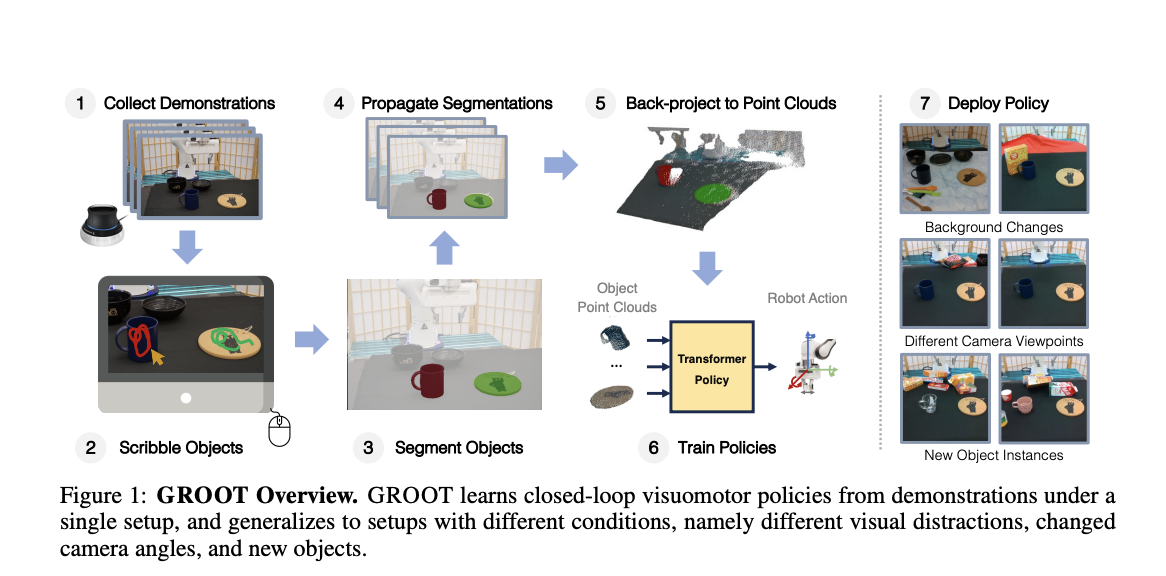
When a whirring sound catches your attention, you’re walking down the bustling city street, carefully cradling your morning coffee. Suddenly, a knee-high delivery robot zips past you on the crowded sidewalk. With remarkable dexterity, it smoothly avoids colliding into pedestrians, strollers, and obstructions, deftly plotting a clear path forward. This isn’t some sci-fi scene –…